Space mining, the extraction of valuable resources from asteroids, the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies, is emerging as a critical field for the future of space exploration and resource utilization. As Earth’s resources become increasingly strained, space mining offers a sustainable solution to meet the growing demand for materials, while also enabling long-term human presence in space.
Why Space Mining?
Resource Scarcity on Earth
- Depletion of rare metals (e.g., platinum, gold, and rare earth elements) essential for technology and renewable energy.
- High environmental costs of terrestrial mining.
Cost Efficiency for Space Exploration:
- Transporting materials from Earth is prohibitively expensive.
- In-situ resource utilization (ISRU) reduces the need to launch supplies, enabling sustainable missions.
Economic Opportunities:
- Asteroids contain trillions of dollars worth of precious metals and rare materials.
- Potential for new industries and markets in space.
Target Resources
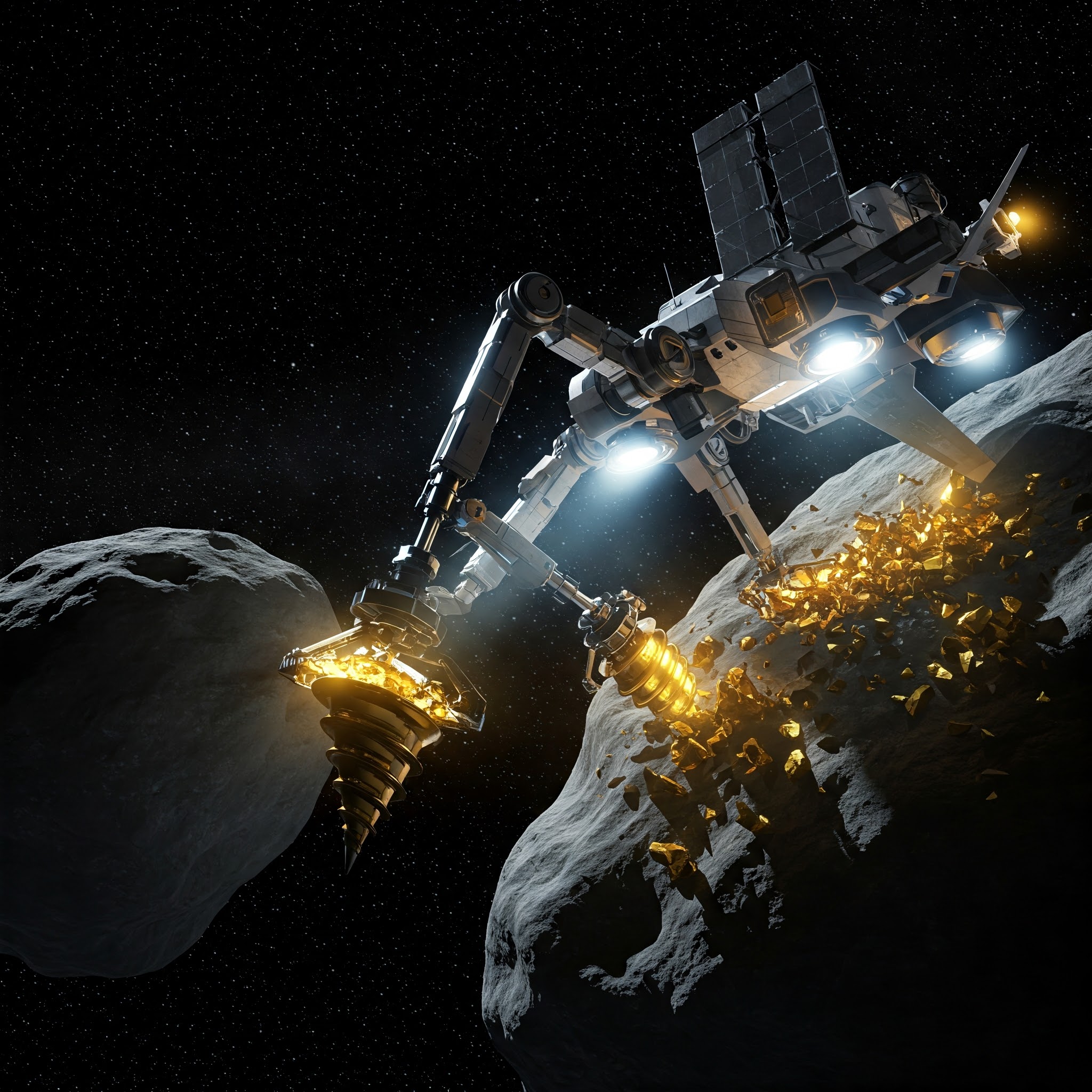
1. Asteroids:
- Metallic Asteroids: Rich in iron, nickel, cobalt, and platinum-group metals.
- Carbonaceous Asteroids: Contain water, carbon, and organic compounds, useful for fuel and life support.
- Silicate Asteroids: Provide silicon and oxygen for construction and manufacturing.
2. The Moon:
- Water Ice: Found in permanently shadowed craters, essential for producing hydrogen and oxygen for fuel.
- Regolith: Contains helium-3 (a potential fuel for nuclear fusion) and metals like aluminum and titanium.
3. Mars:
- Water Ice: Subsurface deposits for drinking water, agriculture, and fuel production.
- Minerals: Iron oxide, silica, and magnesium for construction and manufacturing.
Technological Challenges
1. Exploration and Identification:
- Advanced telescopes and spacecraft to locate resource-rich asteroids.
- Robotic probes for detailed analysis of composition.
2. Extraction Methods:
- Drilling, heating (using solar mirrors), and magnetic separation in microgravity.
- Autonomous robots for mining operations in harsh environments.
3. Processing and Refining:
- Developing techniques to extract and refine materials in space.
- Utilizing 3D printing and ISRU to convert raw materials into usable products.
4. Transportation:
- Returning high-value materials to Earth or transporting resources to space stations and colonies.
- Using mined water to produce rocket fuel for interplanetary travel
Legal and Ethical Considerations
1. Outer Space Treaty (1967):
- Prohibits national sovereignty over celestial bodies but allows resource use.
- Countries like the U.S. and Luxembourg have passed laws permitting private ownership of mined resources.
2. Artemis Accords:
- Promote international cooperation and sustainable practices in space exploration.
3. Ethical Concerns:
- Avoiding contamination of celestial bodies.
- Ensuring equitable access to space resources.
Economic and Environmental Impact
1. Cost:
- High initial investment, but long-term profitability from rare materials and space infrastructure.
- Reduced costs for space missions through ISRU.
2. Market Potentia:
- Precious metals, rare earth elements, and space-based fuel depots.
- Growth of space-based industries like manufacturing and construction.
3. Environmental Benefits:
- Reducing the environmental impact of terrestrial mining.
- Minimizing space debris and preserving celestial environments.
Current Efforts and Missions
1. NASA’s OSIRIS-REx/OSIRIS-APEX:
- Returned samples from asteroid Bennu and is now studying Apophis.
2. JAXA’s Hayabusa2:
- Successfully retrieved samples from asteroid Ryugu.
3. Commercial Ventures:
- Companies like AstroForge, Planetary Resources, and TransAstra are developing technologies for asteroid mining.
Future Prospects
1. In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU):
- Supporting Mars colonies with locally sourced water and fuel.
- Building space habitats and infrastructure using asteroid metals.
2. Space Infrastructure:
- Constructing solar power stations and manufacturing facilities in space.
3. Scientific Advancements:
- Enhancing our understanding of the solar system’s formation and resource distribution.
The Future of Space Mining:
Despite these challenges, the future of space mining looks promising. Several companies and governments are investing in the development of space mining technologies, and the cost of space launch is steadily decreasing. In the coming decades, we may see the first commercial space mining operations taking place.
Space mining has the potential to revolutionize our relationship with space and with the resources we need to sustain our civilization. It could provide us with access to valuable resources, enable further space exploration, and even help us to address some of the environmental challenges we face on Earth. While it is still a nascent industry, space mining is an exciting frontier with the potential to transform our future
Space mining represents a transformative opportunity for humanity, enabling sustainable space exploration, economic growth, and technological innovation. While significant challenges remain, advancements in robotics, space technology, and international cooperation are paving the way for a new era of space industrialization. By responsibly harnessing the resources of the cosmos, we can ensure a prosperous future both on Earth and beyond.